Sales Compensation Calculation (Factors, Formula and Tools)


Often, compensation is linked to salary. However, salary is a salesperson’s wage, and compensation is a comprehensive view of all the benefits provided by the company. It depends on factors like industry, years of experience, location, skillset, and supply and demand. Read on to learn more about calculating compensation both manually and using online tools.
Salary ≠ Total compensation
If I were to define it, sales compensation is the sum of salary, training cost, benefits, and other incentives a salesperson might receive when they join an organization. In other words, it is the total cost an employer spends on an employee.
Incentives can range from free coffee coupons and paid time off to health insurance coverage and development allowances. So how do you calculate all of this?
In this article, I’ll cover the five key factors of compensation calculations and how to calculate them
Here is what a compensation generally comprises of:
Let’s see how you can do calculations:
Here’s a step-by-step method on how you can arrive at a number
Step 1: Calculate the base salary
Base salary is the annual salary which is divided by pay periods.
For example, if your employee receives $40,000 annually and you pay them monthly, then you need to divide $40,000 by 12. This results in $3,333.3 as the base salary.
Step 2: Calculate the commission/ incentive
Assume the commission/incentive is 10% of the revenue generated. Let's say $5000 is the revenue, and $500 is the commission/incentive
Step 3: Calculate the bonus
Any bonus you have planned for the financial year should be taken into consideration. Let's say you are giving a $500 bonus on target exceeded by 20%. I
In this case, you have to assume the salesperson will hit the target and take it into calculation.
For a realistic internal projection, you can look at the historic data and see how many of your sales folks exceed target by 20%.
Step 4: Calculate the reimbursements
Take into consideration the maximum caps of reimbursements. It is possible that an employee will not spend the entirety. However, for calculation, you need to take the maximum limit you will reimburse.
For example, $100/mo for fuel and $100/yr for L&D.
Step 5: Calculate the benefits
PTO: To calculate paid leave, you need to multiply the number of paid leaves by the daily earnings of the person.
For example, if you have 20 days of paid leave, your daily wage is 109.5 ($40,000/365). Next, you need to multiply it by the number of paid leaves, which is 20*109.5 = $2190.
Health insurance: Calculate based on how much you are paying per employee. To do this, divide total premium by number of employees. Let's assume $40
Stock options: If you are offering $10000 worth of stock or ESOPs, take that into account.
Step 6: Perform final calculations
Base salary + Commission + bonus + reimbursements (fuel + L&D allowances) + benefits (insurance + PTO + stock options).
$40,000 + $6000+ $500 + $1200 + $100 + $2190 + $10000 = $59,990
You can include any allowance to this as per your business.
Let’s take a look at various factors that shape sales compensation:
Salespeople can earn different compensation packages depending on the industry they work in.
For example, a person working as an entry-level sales representative at a manufacturing company will be compensated less than a person working as an entry-level sales representative at an IT company. It is easily a $20,000 gap in the average pay.
Moreover, the compensation packages depend on:
These factors also help determine if the job is more labor-oriented or knowledge-based.
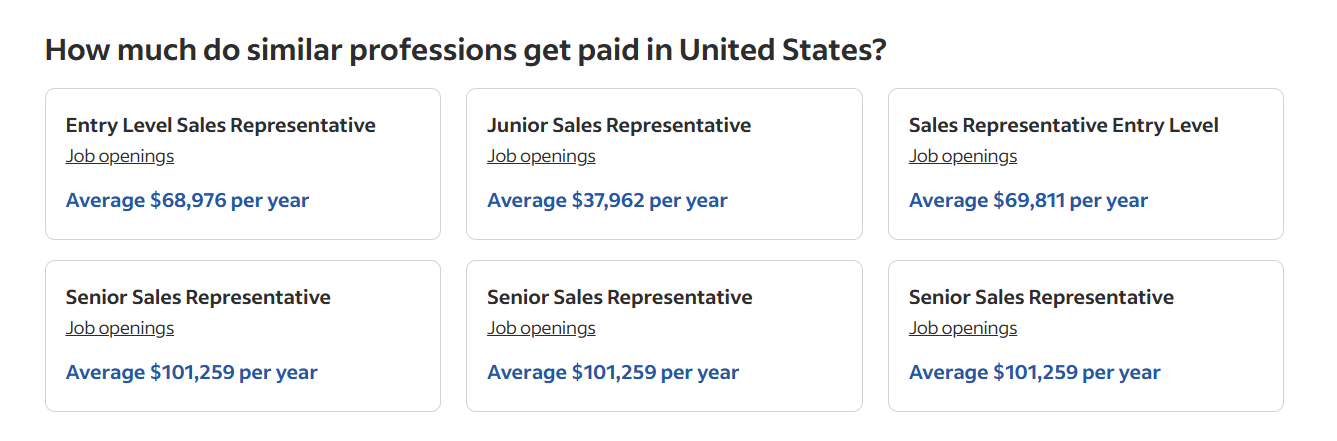
Another metric that is crucial to compensation is the years of experience of the salesperson. The more education and work experience the candidate has, the more they’re compensated.
For example, if you’re looking to hire a sales representative with 5 years of experience in catering to enterprise leads. Then you need to pay them better with a more competitive and comprehensive package.
This image show how the salary increases with the seniorty of the role aka years of experience.
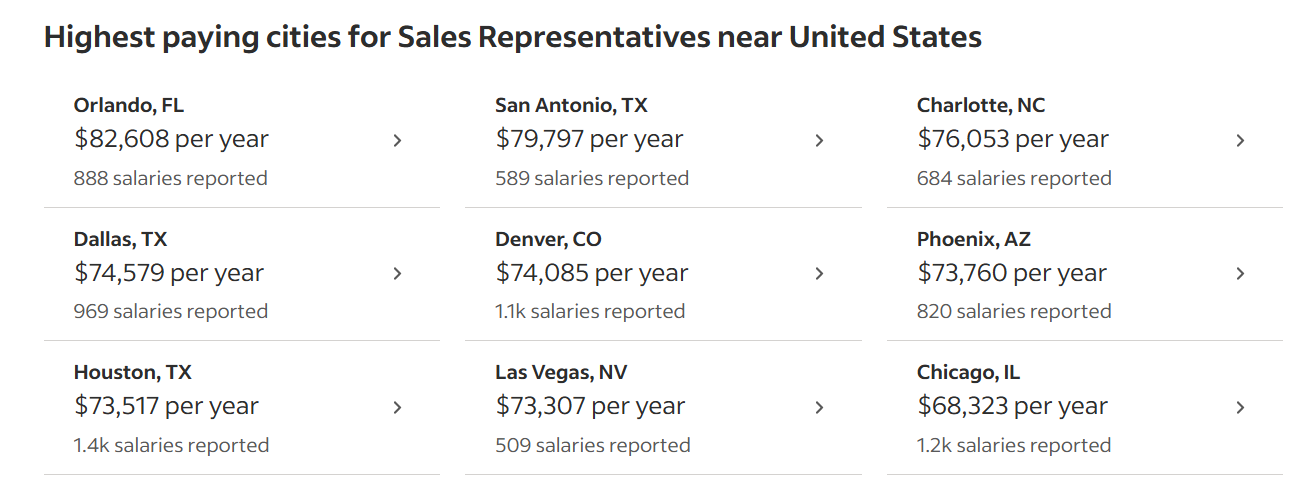
Compensation packages even if in the same industry and with the same years of experience vary vastly with the location.
For instance, an employee with five years of experience in New York City might be getting more than five times the sales rep with the same years of experience in North Carolina.
But remember, location-dependent compensations should adhere to state or country laws. It should also be in line with the employee benchmark metrics set by the respective place.
Different jobs require different skill sets.
Skill sets can also vary depending on the size of the company and industry.
For example, an established organization might need a sales representative who has 5 years of sales experience. On the other hand, an agile company or startup in B2B SaaS will look for a representative who has experience in SDR, sales, specifically in B2B SaaS, and team management. Similarly, skillset requirements for pharma and SaaS will be different.
In these cases, compensations can differ in accordance with the requirements of the business and role.
Lastly, compensations also depend on the talent density for a particular role or even the availability of the role in that location.
Moreover, at times supply and demand for a particular role can outweigh the years of experience or skill set. In these cases, you not only have to pay a lump sum but also give an attractive package to make them stay.
Now that you know how to calculate manually, you can also do it online. It makes life very easy and saves time and money, which you would’ve otherwise spent on buying software.
Here are two online calculators you can use for your compensation calculations
A. Gitlab Calculator
Gitlab calculator is based on a simple formula.
It is optimized to calculate compensations for 200+ regions around the world, based on the formula that people with the same attributes should earn similarly. It is also adjusted to the local currency and provides the closest competitive rate possible.
Note: You need a Gitlab account to use this calculator.
B. CalcXML
CalcXML is a free-to-use calculator that is based on attributes like
This calculation helps you analyze the financial needs required to hire an employee.
A sales incentive management software allows you to automate commission/incentive calculation. Commission calculation can be difficult if its structure is complex and there are many variables such as tiers, clawback, retention, roll- up, multi-year deals, etc.
The software will pull necessary data from your CRM or spreadsheet or anything tool that you use. On the platform, you can write the commission logic, set teams and hierarchies, add quotas and more.
Creating role-based compensation packages will protect your salespeople and company against unwanted economic downturns.
That’s why it’s important to understand the factors to come up with an effective compensation plan.
Compensation calculation inculcates a culture of transparency and streamlines collaboration. It also shows that you care about your salesforce’s success and are willing to reward them as they scale.
Use the methods shown above to pick what suits your team the best!